|
Size: 4154
Comment:
|
Size: 7774
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| <<TableOfContents(4)>> | #rev 2018-10-15 bonaccos ## page was renamed from Services/FileAccess/FileSystemAccess <<TableOfContents()>> |
| Line 3: | Line 5: |
| = The Transparent Remote File-System Access Method = An alternative to the explicit transfer of files from one machine to another is to attach the remote filesystem to the local machine such that all programs can access it as if it was just another local partition. There are several solutions to this problem, the classical examples are NFS and AFS. At the ETH we are using both of them extensively. Unfortunately NFS has security issues which prevent it from being used in an open environment, and AFS requires special (complex) software on the client side and fundamental changes in the setup of servers. We therefore currently recommend '''Samba''' for remote filesystem attachment. Samba is a free implementation of the Microsoft File Sharing Protocol (SMB). We are running it on all our Unix servers. This enables Windows computers to access files on the Unix machines as if they were on a normal Windows server. Linux is also able to access Samba and mount it just like any other file system. SMB does not encrypt the data it transfers (unlike SSH) but it uses a special method for password authentication which protects the privacy of the password. |
== Accessing Samba shares from Linux == === Overview === Recent Linux Kernels contain the userspace filesystem FUSE. This allows you to use all sorts of new an inovative ways for mounting remote fileystems with normal user privileges. Samples are the "gnome userspace virtual filesystem" and "sshfs" based on SSH. |
| Line 6: | Line 9: |
| All graphical desktop file managers must use FUSE based solutions to access remote SMB/CIFS filesystems because they are running with normal user privileges. | |
| Line 7: | Line 11: |
| == Accessing Samba shares from Linux with Konqueror (all machines at ETH) == Open your Konqueror Filemanager/Webbrowser. |
'''In all cases, the share will be mounted in:''' {{{ /run/user/$UID/gvfs/smb-share:server=X,share=Y }}} |
| Line 10: | Line 16: |
| As location, use smb://server/directory followed by <Enter>Type your username and password in the following dialog box. | in order to be able to access from the command line.<<BR>> |
| Line 12: | Line 18: |
| For accessing your share provided from ID, use the following data: | As documented in [[Workstations/FindYourData]] the share `//itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/$USER` is a good place to find all your accessible CIFS resources. Technical this share is an implementation of a "Distributed File System (DFS)" root for your account. Unfortunately not all desktop file managers can handle this special kind of a share. With the KDE file managers Konqueror and Dolphin you can't use this share (see [[Services/FileAccess/CIFSLinux#KDE_Konqueror.2CDolphin|Konqueror, Dolphin]]). === Protocol configuration === Recent Debian releases limit the maximum protocol version of Samba to a lower version than commonly offered by modern Windows servers. This is easily remedied by creating a minimal Samba configuration with the following string of commands: {{{#!highlight bash mkdir ~/.smb && echo -e '[global]\nmax client protocol = SMB3' > ~/.smb/smb.conf }}} === Command Line === ==== gvfs-mount ==== You can also connect to a Samba share on the command line. After you run that command, you can browse the share in Nautilus. |
| Line 15: | Line 31: |
| Location: smb://nas-nethz-users.ethz.ch/share-u-$/username Username: d\yourNethzUsername Password: yourPrivatePassword |
pmuster@testclient:~> gvfs-mount smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster Password required for share pmuster on itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch User [pmuster]: pmuster Domain [WORKGROUP]: d Password: ******** }}} |
| Line 19: | Line 38: |
| Obs! The 'share-u-$' part of the location is dependant on the first character in your username. If your username is 'kpelle', this part of the location will change to 'share-k-$' }}} For accessing your D-ITET share, user the following: |
To unmount a share on the command line, just add the {{{-u}}} flag: |
| Line 24: | Line 41: |
| Location: smb://homes.ee.ethz.ch/username Username: d\username Password: yourPrivatePassword |
pmuster@testclient:~> gvfs-mount -u smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster |
| Line 29: | Line 44: |
| ==== smbclient ==== smbclient is something like an interactive shell to the file server and also a good troubleshooting tool for connection problems. To connect your personal DFS root share enter: {{{ pmuster@testclient:~$ smbclient -W d //itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster Enter pmuster's password: Domain=[D] OS=[Windows 6.1] Server=[Samba 4.2.10-Debian] smb: \> smb: \> ls . D 0 Thu Oct 13 15:27:09 2016 .. D 0 Thu Nov 24 04:55:59 2016 home D 0 Thu Oct 13 15:27:09 2016 project01 D 0 Thu Oct 13 15.27:09 2016 |
|
| Line 30: | Line 57: |
| == Using CIFS to connect to Samba shares == You can also mount your Samba home area with CIFS. This method is only available on computers where you have root access (i.e. this does not work on Linux workstations managed by us). '''If the command returns an error message saying "wrong fs type", make sure the package "cifs-utils" is installed.''' |
47929224 blocks of size 1024. 37295664 blocks available smb: \> cd home smb: \home\> smb: \home\> ls . D 0 Thu Nov 24 09:35:24 2016 .. DA 0 Thu Nov 24 08:17:38 2016 public_html D 0 Wed Feb 3 15:34:27 2016 Desktop D 0 Mon May 23 14:57:56 2016 Downloads D 0 Mon May 23 14:50:26 2016 .... 1536000 blocks of size 1024. 1340637 blocks available smb: \home\> exit pmuster@testclient:~$ }}} With the command `help` you get a list of all available commands inside the shell. ==== root mount ==== You can also mount your Samba home area with CIFS. This method is only available on computers where you have root access (i.e. this does not work on Linux workstations managed by us). '''If the command returns an error message saying "wrong fs type", make sure the packages "cifs-utils" and "keyutils" are installed.''' |
| Line 35: | Line 79: |
| # mkdir /tardis-home # mount -t cifs -o user=<d\your_tardis_login>,name=homes.ee.ethz.ch \\\\homes.ee.ethz.ch\\<d\your_tardis_login> /tardis-home |
# mkdir /itet-stor # mount -t cifs -o user=<nethz_login>,domain=d //itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/<nethz_login> /itet-stor |
| Line 38: | Line 82: |
| Recent Linux Kernels contain the userspace filesystem [[http://fuse.sourceforge.net/|FUSE]]. This allows you to use all sorts of new an inovative ways for mounting remote fileystems ... for example you can mount a file system via an ssh connection without needing root privileges: | |
| Line 40: | Line 83: |
| === Desktop File Managers === ==== Gnome Nautilus ==== Select on the left side '''Connect to network''' and enter the name of the share in the '''Server Address''' field, e.g. as `smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster`. Enter the details as given in the screenshot below. {{attachment:nautilus.png}} ==== Cinnamon Nemo ==== Open the {{{Connect to Server}}} application and enter the details similar to the screenshot below. {{attachment:nemo.png}} ==== KDE Konqueror,Dolphin ==== As mentioned above Konqueror and Dolphin can't be used to access smb resources over `\\itet-stor\username`. Open your Konqueror or Dolphin Filemanager/Webbrowser. As location, use `smb://server/share` followed by `<Enter>`. Type your username and password in the following dialog box. ===== ID home share ===== '''{{{ Location: smb://nas-nethz-users.ethz.ch/share-<?>-$/username Username: d\yourNethzUsername Password: yourPrivatePassword }}}''' The '''share-<?>-$''' part of the location is dependant on the first character in your username. If your username is '''kpelle''', this part of the location must be changed to '''share-k-$'''. ===== D-ITET home share ===== '''{{{ Location: smb://nas-itet-01/itet_isg_homes_<nn>/username Username: d\username Password: yourPrivatePassword }}}''' The homes are distributed over multiple `itet_isg_homes_<nn>` shares, to see the number to use you can look at the NFS path of your home: {{{ pmuster@testclient:~$ ssh login.ee.ethz.ch "df ." pmu@login.ee.ethz.ch's password: Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on nas-itet-01.ethz.ch:/sco_itet_005/itet_isg_homes_03/pmuster 1536000 195072 1340928 13% /home/pmuster pmuster@testclient:~$ }}} So the location for pmuster's home is: smb://nas-itet-01/itet_isg_homes_03/pmuster. ===== D-ITET project share ===== '''{{{ Location: smb://itetnas<nn>.ee.ethz.ch/project Username: d\username Password: yourPrivatePassword }}}''' Again the NFS path of the project home is needed: {{{ pmuster@testclient:~$ ssh login.ee.ethz.ch "df /home/mare" Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on itetnas02:/usr/itetnas02/data-project-01/mare 3170549760 620497920 2539297792 20% /home/mare pmuster@testclient:~$ }}} So the location for the mare project home is: `smb://itetnas02.ee.ethz.ch/mare`. === Troubleshooting === Depending on the way of accessing a Samba share, error messages similar to the following might appear: * '''gvsf-mount''': `Error mounting location: Failed to mount Windows share: Connection timed out` * '''nautilus''': `Unhandled error message: Failed to mount Windows share: Connection timed out` * '''smbclient''': `protocol negotiation failed: NT_STATUS_CONNECTION_RESET` This indicates a failed protocol negotiation between the Samba server and your client in case the protocol version offerd by the server is higher than the client accepts. To fix this apply the protocol configuration mentioned above. '''smbclient''' accepts the parameter "-m" to set the protocol level directly without the need to apply the protocol configuration: {{{ pmuster@testclient:~$ smbclient -W d -m SMB3 //itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster }}} == SSH File System == |
|
| Line 51: | Line 170: |
| Line 53: | Line 173: |
| == Windows Network Drive == You can access your home directory by mounting {{{\\homes.ee.ethz.ch\username}}} as network drive in Windows. If you do this from outside ETH, you need to create a [[http://computing.ee.ethz.ch/Workstations/Network/VPN | VPN connection]] first. Click on the Computer shortcut and then click on the 'Map network drive' button from the upper toolbar. Select the drive letter you want to use for this mapping. The Address to your folder is \\homes.ee.ethz.ch\YOUR-USERNAME. Im this example its pmeier. Replace pmeier with your username. Set the Checkbox "Connect using different credentials" and if you want, set "Reconnect at logon". Click on finish. {{attachment:WindowsNetworkDrive1.png}} On the next screen, Enter d\YOUR-USERNAME and Enter your password. When done, click on OK. {{attachment:WindowsNetworkDrive2.png}} If the mapping process worked fine, the newly created drive will open and will become available. |
Contents
Accessing Samba shares from Linux
Overview
Recent Linux Kernels contain the userspace filesystem FUSE. This allows you to use all sorts of new an inovative ways for mounting remote fileystems with normal user privileges. Samples are the "gnome userspace virtual filesystem" and "sshfs" based on SSH.
All graphical desktop file managers must use FUSE based solutions to access remote SMB/CIFS filesystems because they are running with normal user privileges.
In all cases, the share will be mounted in:
/run/user/$UID/gvfs/smb-share:server=X,share=Y
in order to be able to access from the command line.
As documented in Workstations/FindYourData the share //itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/$USER is a good place to find all your accessible CIFS resources. Technical this share is an implementation of a "Distributed File System (DFS)" root for your account. Unfortunately not all desktop file managers can handle this special kind of a share. With the KDE file managers Konqueror and Dolphin you can't use this share (see Konqueror, Dolphin).
Protocol configuration
Recent Debian releases limit the maximum protocol version of Samba to a lower version than commonly offered by modern Windows servers. This is easily remedied by creating a minimal Samba configuration with the following string of commands:
1 mkdir ~/.smb && echo -e '[global]\nmax client protocol = SMB3' > ~/.smb/smb.conf
Command Line
gvfs-mount
You can also connect to a Samba share on the command line. After you run that command, you can browse the share in Nautilus.
pmuster@testclient:~> gvfs-mount smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster Password required for share pmuster on itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch User [pmuster]: pmuster Domain [WORKGROUP]: d Password: ********
To unmount a share on the command line, just add the -u flag:
pmuster@testclient:~> gvfs-mount -u smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster
smbclient
smbclient is something like an interactive shell to the file server and also a good troubleshooting tool for connection problems. To connect your personal DFS root share enter:
pmuster@testclient:~$ smbclient -W d //itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster
Enter pmuster's password:
Domain=[D] OS=[Windows 6.1] Server=[Samba 4.2.10-Debian]
smb: \>
smb: \> ls
. D 0 Thu Oct 13 15:27:09 2016
.. D 0 Thu Nov 24 04:55:59 2016
home D 0 Thu Oct 13 15:27:09 2016
project01 D 0 Thu Oct 13 15.27:09 2016
47929224 blocks of size 1024. 37295664 blocks available
smb: \> cd home
smb: \home\>
smb: \home\> ls
. D 0 Thu Nov 24 09:35:24 2016
.. DA 0 Thu Nov 24 08:17:38 2016
public_html D 0 Wed Feb 3 15:34:27 2016
Desktop D 0 Mon May 23 14:57:56 2016
Downloads D 0 Mon May 23 14:50:26 2016
....
1536000 blocks of size 1024. 1340637 blocks available
smb: \home\> exit
pmuster@testclient:~$ With the command help you get a list of all available commands inside the shell.
root mount
You can also mount your Samba home area with CIFS. This method is only available on computers where you have root access (i.e. this does not work on Linux workstations managed by us). If the command returns an error message saying "wrong fs type", make sure the packages "cifs-utils" and "keyutils" are installed.
$ sudo su # mkdir /itet-stor # mount -t cifs -o user=<nethz_login>,domain=d //itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/<nethz_login> /itet-stor
Desktop File Managers
Gnome Nautilus
Select on the left side Connect to network and enter the name of the share in the Server Address field, e.g. as smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster.
Enter the details as given in the screenshot below.
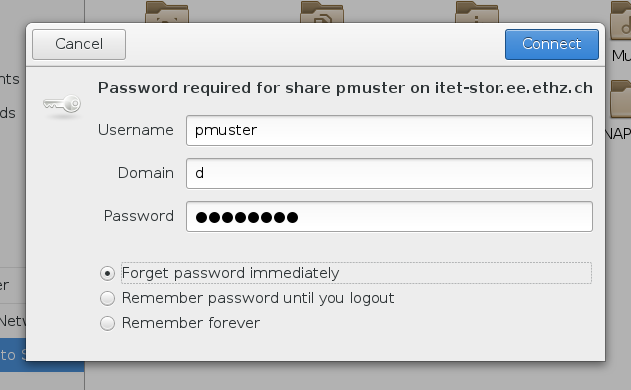
Cinnamon Nemo
Open the Connect to Server application and enter the details similar to the screenshot below.
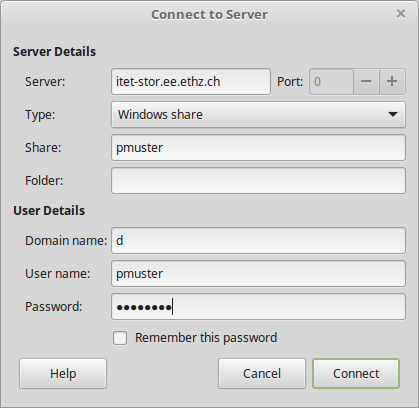
KDE Konqueror,Dolphin
As mentioned above Konqueror and Dolphin can't be used to access smb resources over \\itet-stor\username.
Open your Konqueror or Dolphin Filemanager/Webbrowser.
As location, use smb://server/share followed by <Enter>. Type your username and password in the following dialog box.
ID home share
Location: smb://nas-nethz-users.ethz.ch/share-<?>-$/username
Username: d\yourNethzUsername
Password: yourPrivatePassword
The share-<?>-$ part of the location is dependant on the first character in your username. If your username is kpelle, this part of the location must be changed to share-k-$.
D-ITET home share
Location: smb://nas-itet-01/itet_isg_homes_<nn>/username
Username: d\username
Password: yourPrivatePassword
The homes are distributed over multiple itet_isg_homes_<nn> shares, to see the number to use you can look at the NFS path of your home:
pmuster@testclient:~$ ssh login.ee.ethz.ch "df ." pmu@login.ee.ethz.ch's password: Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on nas-itet-01.ethz.ch:/sco_itet_005/itet_isg_homes_03/pmuster 1536000 195072 1340928 13% /home/pmuster pmuster@testclient:~$
So the location for pmuster's home is: smb://nas-itet-01/itet_isg_homes_03/pmuster.
D-ITET project share
Location: smb://itetnas<nn>.ee.ethz.ch/project
Username: d\username
Password: yourPrivatePassword
Again the NFS path of the project home is needed:
pmuster@testclient:~$ ssh login.ee.ethz.ch "df /home/mare" Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on itetnas02:/usr/itetnas02/data-project-01/mare 3170549760 620497920 2539297792 20% /home/mare pmuster@testclient:~$
So the location for the mare project home is: smb://itetnas02.ee.ethz.ch/mare.
Troubleshooting
Depending on the way of accessing a Samba share, error messages similar to the following might appear:
gvsf-mount: Error mounting location: Failed to mount Windows share: Connection timed out
nautilus: Unhandled error message: Failed to mount Windows share: Connection timed out
smbclient: protocol negotiation failed: NT_STATUS_CONNECTION_RESET
This indicates a failed protocol negotiation between the Samba server and your client in case the protocol version offerd by the server is higher than the client accepts. To fix this apply the protocol configuration mentioned above.
smbclient accepts the parameter "-m" to set the protocol level directly without the need to apply the protocol configuration:
pmuster@testclient:~$ smbclient -W d -m SMB3 //itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster
SSH File System
$ mkdir ~/tardis-home $ sshfs <d\your_tardis_login>@login.ee.ethz.ch: ~/tardis-home
But please note, that you can't do sshfs on homes.ee.ethz.ch - use login.ee.ethz.ch instead!
You can also unmount it again by typing:
$ fusermount -u ~/tardis-home
Please note that sshfs is not officially supported by the ISG.EE