|
Size: 5996
Comment:
|
Size: 6044
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 52: | Line 52: |
| * This will show you the ip addresses of all network interfaces. Have a look at the screenshot below to get an idea how to find the right IP address in the output. Usually there are only two interfaces, `lo` (loopback, not relevant), and the other interface, `ens33` in the example, which will be the relevant interface. The relevant line begins with `inet` followed by the IP address. If that line is missing, if the IP adress contains only zeroes or is something else than 192.168.x.y or 10.0.x.y, then something might be wrong with the network configuration. {{attachment:ip_addr.jpg}} |
* This will show you the ip addresses of all network interfaces. Have a look at the screenshot below to get an idea how to find the right IP address in the output. Usually there are only two interfaces, `lo` (loopback, not relevant), and the other interface, `ens33` in the example, which will be the relevant interface. The relevant line begins with `inet` followed by the IP address. If that line is missing, if the IP adress contains only zeroes or is something else than 192.168.x.y or 10.0.x.y, then something might be wrong with the network configuration. {{attachment:ip_addr.jpg}} * As soon as you know the IP address, 192.168. |
Singularity Builder VM
Singularity Builder VM is an easy-to-install virtual machine running a mininmal Debian Linux installation prepared with Sylabs Singularity, allowing to build Singularity images as root user in a sandbox environment. The Builder VM is preconfigured to exchange data between some host and guest file systems. The Builder VM in its current concept may only be used on (managed) Linux computers.
Installation
You can use any ISG.EE managed computer to perform the following steps:
- Open a Linux terminal
Enter sgbuilder. This will show you an overview/ help on how to install and start the Singularity Builder VM.
Create a new VM copy of the Singularity Builder VM in any directory you like, e.g. /scratch/<Your_Username>/<VM1>:
sgbuilder install default /scratch/Your_Username/VM1
Please note you should install your VM somewhere in /scratch and not in your user home directory for performance reasons.Once the VM has been installed, you can start it up as many times as you want using:
sgbuilder start /scratch/Your_Username/VM1
- To shut down the VM in a clean manner, enter "shutdown now" at the shell.
Usage
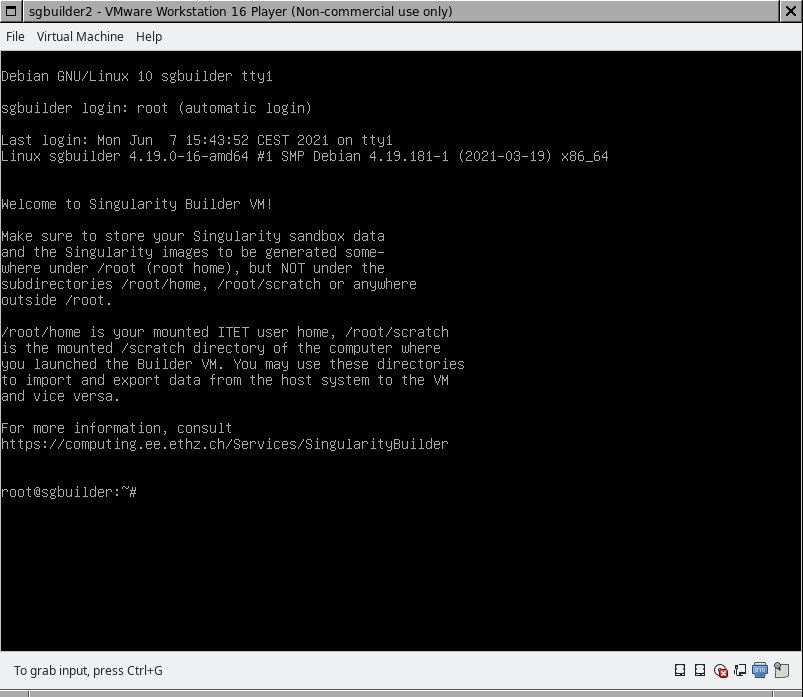
- Startup the Builder VM as described in the Installation section above. The following window appears after some startup seconds.
/root will be the current working directory right after VM startup. This is a 30 GB virtual disk within the VM that can be used to save newly generated Singularity images or a Singularity image sandbox.
/root/home is your ITET user home. This can be used to import or export data (e.g. generated SIF images) from the VM to your regular user home directory and vice versa.
/root/scratch is the /scratch directory of the Linux (host system) computer where you started up the VM using sgbuilder start. This can be used to import or export data from the VM to your computer's /scratch directory and vice versa.
When using Singularity, always ensure the output path (e.g the sandbox directory or Singularity image output location) is somewhere below /root. DO NOT ATTEMPT to save Singularity sandbox data or images directly to /root/home or /root/scratch or any other directory above /root (like the root user's home). Saving Singularity output data directly to the scratch or home won't work, as you cannot store any files there using other user id's or group id's than your own id's. Storing data above /root won't work because that would be on the VM's operating file system disk which has - intentionally - almost no diskspace left.
- That said, the idea is to use the VM as follows: first import all data needed from external filesystems into the VM's filesystem. Then do your Singularity image processing and at the end, export the generated Singularity image to an external filesystem.
Tips & tricks
Changing the VM's keyboard settings
The default keyboard setting is "us" (american english keyboard). If you want to change this setting permanently (across reboots), you can edit
/etc/default/keyboard
within the VM and set another country code, e.g. "ch" for Swiss German keyboards. To make the change immediately effective without rebooting the VM, you can enter
setupcon <keymapcode> e.g. setupcon ch
Accessing the VM from outside
Sometimes you want to copy-paste text from your Linux desktop to the Singularity Builder VM console. You may have noticed however, that copy/ paste from/ to the VM console window does not work. As a workaround, you might access the VM's shell from outside the VM using the VM's ssh or serial console feature. We recommend using ssh, because ssh clients support higher-level terminal emulation, which is often not the case with standard tools for serial console access.
Accessing the VM through ssh
To make this work, you will first have to set a password for the root user
root@sgbuilder:~# passwd New password: ....... Retype new password: ....... passwd: password updated successfully
Then you have to find out the VM's current private IP address. This IP address might change across VM startups/ reboots and must therefore be looked up again after each VM restart. You will find the IP address as follows
root@sgbuilder:#~ ip addr
This will show you the ip addresses of all network interfaces. Have a look at the screenshot below to get an idea how to find the right IP address in the output. Usually there are only two interfaces, lo (loopback, not relevant), and the other interface, ens33 in the example, which will be the relevant interface. The relevant line begins with inet followed by the IP address. If that line is missing, if the IP adress contains only zeroes or is something else than 192.168.x.y or 10.0.x.y, then something might be wrong with the network configuration.
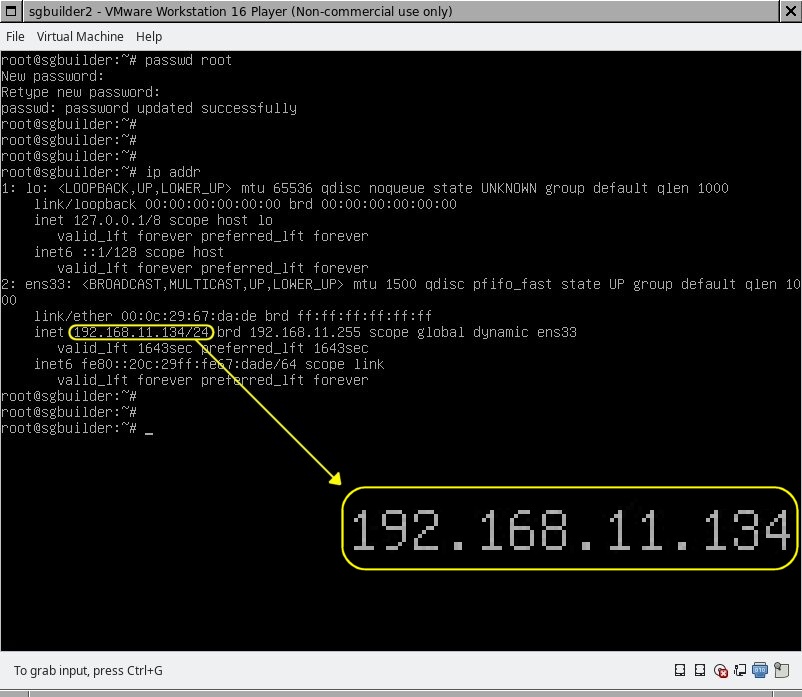
- As soon as you know the IP address, 192.168.
Accessing the VM through serial console
You can access the VM's console from any Linux terminal as follows (example):
socat - /scratch/Your_Username/VM1/sgbuilder.sock
NOTE: /scratch/Your_Username/VM1 is the path to your VM installation as described above in the "Installation" section
NOTE: Terminal emulation in serial console does not work very well. You might enter
stty -echo
to disable echoing your inputs twice on each line entered.
The VM cannot access the network, because it has no IP address
Usually, the IP address is automatically assigned during the VM startup. You may check this entering ip addr within the VM. The network interface used for external connections is ususally named ensNN, e.g. ens33. If it doesn't have a valid IPv4 address, you may either reboot the VM or try to obtain a new IP without rebooting, using dhclient <interfacename>. In our example, the <interfacename> would be ens33.