|
Size: 4197
Comment:
|
Size: 3416
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| = The Transparent Remote File-System Access Method = An alternative to the explicit transfer of files from one machine to another is to attach the remote filesystem to the local machine such that all programs can access it as if it was just another local partition. There are several solutions to this problem, the classical examples are NFS and AFS. At the ETH we are using both of them extensively. Unfortunately NFS has security issues which prevent it from being used in an open environment, and AFS requires special (complex) software on the client side and fundamental changes in the setup of servers. We therefore currently recommend '''Samba''' for remote filesystem attachment. Samba is a free implementation of the Microsoft File Sharing Protocol (SMB). We are running it on all our Unix servers. This enables Windows computers to access files on the Unix machines as if they were on a normal Windows server. Linux is also able to access Samba and mount it just like any other file system. SMB does not encrypt the data it transfers (unlike SSH) but it uses a special method for password authentication which protects the privacy of the password. |
## page was renamed from Services/FileAccess/FileSystemAccess <<TableOfContents()>> |
| Line 4: | Line 4: |
| <<TableOfContents(3)>> | == Accessing Samba shares from Linux == === Overview === Recent Linux Kernels contain the userspace filesystem FUSE. This allows you to use all sorts of new an inovative ways for mounting remote fileystems with normal user privileges. Samples are the "gnome userspace virtual filesystem" and "sshfs" based on SSH.<<BR>><<BR>> All graphical desktop file managers must use FUSE based solutions to access remote SMB/CIFS filesystems because they are running with normal user privileges.<<BR>><<BR>> In all cases, the share will be mounted in `/run/user/$UID/gvfs/smb-share:server=X,share=Y` so that you can also access it on the command line. === Command Line === ==== gvfs-mount ==== You can also connect to a Samba share on the command line. After you run that command, you can browse the share in Nautilus. {{{ pmuster@testclient:~> gvfs-mount smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster Password required for share pmuster on itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch User [pmuster]: pmuster Domain [WORKGROUP]: d Password: ******** }}} To unmount a share on the command line, just add the {{{-u}}} flag: {{{ pmuster@testclient:~> gvfs-mount -u smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster }}} |
| Line 7: | Line 30: |
| == The Samba Password == Samba (SMB) uses a fundamentally different way to handle passwords than Unix. This has the advantage that passwords do not cross the net unencrypted, but it has the big disadvantage that we have to maintain a separate password database for Samba. We have setup our system so that the Samba password gets changed at the same time as the unix password. If your samba password does not work, please contact support@ee.ethz.ch . First, note, that all the information below assumes that you have Windows NT, 2000 or XP installed. With this out of the way you just open the '''start''' menu, select '''Run ...''' and type: {{{ net use * \\homes.ee.ethz.ch\login * /user:login }}} Replace ''login'' with your Tardis login name and press return. Now a pop-up will ask for your login name (again) and your (samba)password. Once you have entered them, an explorer will open which shows the content of your Tardis home directory. You can now use the same syntax to access the Tardis home directly from within applications. You can also create a shortcut on the desktop which points to this address to make access even simpler. Note that if you use the same user-name and (samba)password on Windows as you use on Tardis, then windows will not ask you again for your password when mounting the Tardis home. == Using Samba from Linux == From Linux you can use the normal '''mount''' command for mounting Samba shares: |
==== root mount ==== You can also mount your Samba home area with CIFS. This method is only available on computers where you have root access (i.e. this does not work on Linux workstations managed by us). '''If the command returns an error message saying "wrong fs type", make sure the package "cifs-utils" is installed.''' |
| Line 22: | Line 36: |
| # mount -t smbfs -o user=lanserc,name=homes.ee.ethz.ch \\\\homes.ee.ethz.ch\\lanserc /tardis-home}}} When you execute the command you will be asked for your (samba)password and then your home will be available under '''/tardis-home'''. Because mounting generally requires root access, the whole process is a bit tedious because you have to become root first. There is shortcut though. You can add an appropriate line to the '''/etc/fstab''' file which will allow users to mount your Tardis home with '''mount /tardis-home''': |
# mount -t cifs -o user=<d\your_tardis_login>,name=homes.ee.ethz.ch \\\\homes.ee.ethz.ch\\<d\your_tardis_login> /tardis-home }}} === Desktop File Managers === ==== Gnome Nautilus ==== Select on the left side '''Connect to network''' and enter the name of the share in the '''Server Address''' field, e.g. as 'smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster'. Enter the details as given in the screenshot below. {{attachment:nautilus.png}} ==== Nemo ==== Open the {{{Connect to Server}}} application and enter the details similar to the screenshot below. {{attachment:nemo.png}} === KDE Konqueror (all machines at ETH) === Open your Konqueror Filemanager/Webbrowser. As location, use smb://server/directory followed by <Enter>Type your username and password in the following dialog box. For accessing your share provided from ID, use the following data: |
| Line 26: | Line 63: |
| [...] //homes.ee.ethz.ch/ smbfs username=lanserc,user,noauto [...] |
Location: smb://nas-nethz-users.ethz.ch/share-u-$/username Username: d\yourNethzUsername Password: yourPrivatePassword Obs! The 'share-u-$' part of the location is dependant on the first character in your username. If your username is 'kpelle', this part of the location will change to 'share-k-$' |
| Line 30: | Line 69: |
| In the man page '''smbmount''' you can find more information about this. == Using CIFS to connect to Samba shares == You can also mount your Samba home area with CIFS: |
For accessing your D-ITET share, user the following: |
| Line 36: | Line 72: |
| $ sudo su # mount -t cifs -o user=lanserc,name=homes.ee.ethz.ch \\\\homes.ee.ethz.ch\\lanserc /tardis-home}}} Recent Linux Kernels contain the userspace filesystem [[http://fuse.sourceforge.net/|FUSE]]. This allows you to use all sorts of new an inovative ways for mounting remote fileystems ... for example you can mount a file system via an ssh connection without needing root privileges: |
Location: smb://homes.ee.ethz.ch/username Username: d\username Password: yourPrivatePassword }}} == SSH File System == |
| Line 42: | Line 81: |
| $ sshfs lanserc@login.ee.ethz.ch: ~/tardis-home | $ sshfs <d\your_tardis_login>@login.ee.ethz.ch: ~/tardis-home |
| Line 49: | Line 88: |
| $ fusermount -u ~/tardis-home}}} | $ fusermount -u ~/tardis-home }}} |
| Line 52: | Line 92: |
---- [[CategoryEDUC]] |
Contents
Accessing Samba shares from Linux
Overview
Recent Linux Kernels contain the userspace filesystem FUSE. This allows you to use all sorts of new an inovative ways for mounting remote fileystems with normal user privileges. Samples are the "gnome userspace virtual filesystem" and "sshfs" based on SSH.
All graphical desktop file managers must use FUSE based solutions to access remote SMB/CIFS filesystems because they are running with normal user privileges.
In all cases, the share will be mounted in /run/user/$UID/gvfs/smb-share:server=X,share=Y so that you can also access it on the command line.
Command Line
gvfs-mount
You can also connect to a Samba share on the command line. After you run that command, you can browse the share in Nautilus.
pmuster@testclient:~> gvfs-mount smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster Password required for share pmuster on itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch User [pmuster]: pmuster Domain [WORKGROUP]: d Password: ********
To unmount a share on the command line, just add the -u flag:
pmuster@testclient:~> gvfs-mount -u smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster
root mount
You can also mount your Samba home area with CIFS. This method is only available on computers where you have root access (i.e. this does not work on Linux workstations managed by us). If the command returns an error message saying "wrong fs type", make sure the package "cifs-utils" is installed.
$ sudo su # mkdir /tardis-home # mount -t cifs -o user=<d\your_tardis_login>,name=homes.ee.ethz.ch \\\\homes.ee.ethz.ch\\<d\your_tardis_login> /tardis-home
Desktop File Managers
Gnome Nautilus
Select on the left side Connect to network and enter the name of the share in the Server Address field, e.g. as 'smb://itet-stor.ee.ethz.ch/pmuster'.
Enter the details as given in the screenshot below.
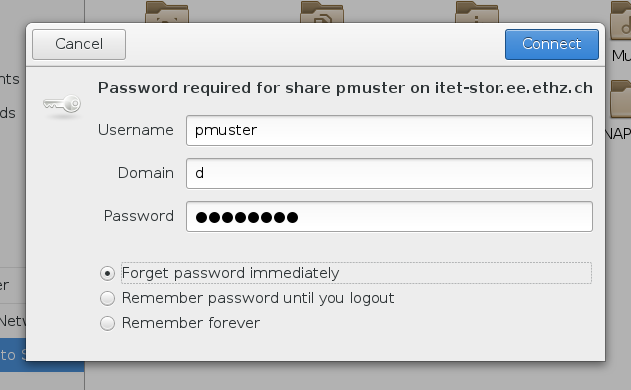
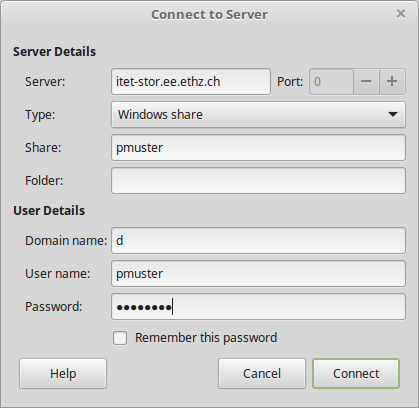
Nemo
Open the Connect to Server application and enter the details similar to the screenshot below.
KDE Konqueror (all machines at ETH)
Open your Konqueror Filemanager/Webbrowser.
As location, use smb://server/directory followed by <Enter>Type your username and password in the following dialog box.
For accessing your share provided from ID, use the following data:
Location: smb://nas-nethz-users.ethz.ch/share-u-$/username Username: d\yourNethzUsername Password: yourPrivatePassword Obs! The 'share-u-$' part of the location is dependant on the first character in your username. If your username is 'kpelle', this part of the location will change to 'share-k-$'
For accessing your D-ITET share, user the following:
Location: smb://homes.ee.ethz.ch/username Username: d\username Password: yourPrivatePassword
SSH File System
$ mkdir ~/tardis-home $ sshfs <d\your_tardis_login>@login.ee.ethz.ch: ~/tardis-home
But please note, that you can't do sshfs on homes.ee.ethz.ch - use login.ee.ethz.ch instead!
You can also unmount it again by typing:
$ fusermount -u ~/tardis-home
Please note that sshfs is not officially supported by the ISG.EE