|
Size: 5620
Comment:
|
Size: 5605
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 10: | Line 10: |
| pmuster@colombo07:~$ pmuster@colombo07:~$ vncserver |
pmuster@zampano:~$ pmuster@zampano:~$ vncserver |
| Line 13: | Line 13: |
| New 'colombo07:7 (pmuster)' desktop is colombo07:7 | New 'zampano:1 (pmuster)' desktop is zampano:1 |
| Line 16: | Line 16: |
| Log file is /home/pmuster/.vnc/colombo07:7.log | Log file is /home/pmuster/.vnc/zampano1.log |
| Line 18: | Line 18: |
| pmuster@colobo07:~$ | pmuster@zampano:~$ |
| Line 20: | Line 20: |
| In the output of the command the number after the colon of the hostname (colomb07:'''7''') is the virtual display number of your vncserver. You need this number to connect your vncviewer to the correct listening port of your vncserver. | In the output of the command the number after the colon of the hostname (zampano:'''1''') is the virtual display number of your vncserver. You need this number to connect your vncviewer to the correct listening port of your vncserver. |
| Line 50: | Line 50: |
| > vncviewer colombo07:7 | > vncviewer zampano:1 |
Contents
What is VNC?
VNC (Virtual Network Computing) is a remote desktop software for several Operating Systems. It can be used for a single graphical application or for a full desktop session. Client and server interact over the Remote Framebuffer (RFB) Protocol. Technically the vncserver process on the target machine is an X-Server with a virtual display attached to it. The vncviewer on the client shows the content of this virtual display in his own window and transfers keyboard and mouse events to the vncserver.
How do I use VNC?
Starting the vncserver
ssh to the target machine and start a vncserver:
pmuster@zampano:~$ pmuster@zampano:~$ vncserver New 'zampano:1 (pmuster)' desktop is zampano:1 Starting applications specified in /home/pmuster/.vnc/xstartup Log file is /home/pmuster/.vnc/zampano1.log pmuster@zampano:~$
In the output of the command the number after the colon of the hostname (zampano:1) is the virtual display number of your vncserver. You need this number to connect your vncviewer to the correct listening port of your vncserver.
If the .vnc subdirectory in your home does not exist in your home it is created at startup and you will be asked to define a password for accessing your server and another one for just observing without interacting. Also created is a default xstartup script which is executed by the vncserver:
xrdb $HOME/.Xresources xsetroot -solid grey export XKL_XMODMAP_DISABLE=1 # select desktop to use /etc/X11/Xsession # starts default desktop on target machine # to select a specific desktop activate one of the desktops stated below # and comment out the line above with /etc/X11/Xsession #/usr/bin/gnome-session #/usr/bin/gnome-session-classic #/usr/bin/startkde #/usr/bin/startxfce4 #/usr/bin/startfluxbox # Automatically end the server process after desktop session logout vncserver -kill $DISPLAY
You can edit the xstartup file to switch to your favorite desktop. The "vncserver -kill" command in the last line stops your vncserver after a logout in the remote desktop session.
Connecting the vncviewer
After the startup you can connect a vncviewer software on your client to your vncserver. On our managed linux clients the command is:
> vncviewer zampano:1
On our managed windows clients we can install the baramundi software RealVNC for you. In the connect-popup window you have to enter the base tcp port number 5900 plus the display number:
RealVNC Viewer is free software and can be downloaded from https://www.realvnc.com .
Terminating a vnc session
As already mentioned above if you are performing a normal desktop logout your vncserver process is killed by the terminating xstartup script and you need to start a new one for the next session. If you only terminate the vncviewer program your vncserver process remains active and you can reconnect your desktop session again.
To manually kill your vncserver on a host ssh to this host and enter the command:
> vncserver -kill :<display number>
VNC access from the internet
Due to security reasons the listening port of the vnc server is not directly reachable from a client in the internet. There are two possibilities to perform a vnc session to an ETH network internal host from the internet :
- Use the Cisco SSL-VPN client software of ID and connect the SSL-VPN adapter before starting the VNC viewer programm
- Access the VNC-server through an SSH-tunnel
VNC through SSH tunnel under Linux
- Start VNC Server on remote host with the option -localhost
$ ssh <remoteHost> // where <remoteHost> is the machine on which the application you want to start runs $ vncserver :<display#> -localhost // where <display#> is a number between 1 and 99
Attention! Always choose a strong password when starting vncserver. Otherwise, you'll make it trivial for intruders to hijack your account!
- Start VNC viewer on your machine (Linux)
$ vncviewer -via <remotehost>.ee.ethz.ch localhost:<display#>
Mac users may establish the tunnel via SSH, then use "open vnc://localhost:PORT" to use the built-in VNC client.
VNC through SSH tunnel under Windows
Start VNC viewer on your machine (Windows with TightVNC and putty)
Putty is the most popular free ssh client software on Windows. When you have configured a normal ssh session to the vnc server machine you can configure additional port forwards on the established ssh-connection. A tunnel configuration needs a local listening port and a destination on ssh server side.The destination could be localhost or another machine reachable by the ssh server machine.
The following screeshots show how to configure an additional tunnel for connecting the local vnc-server on port 5901 of the ssh server machine:
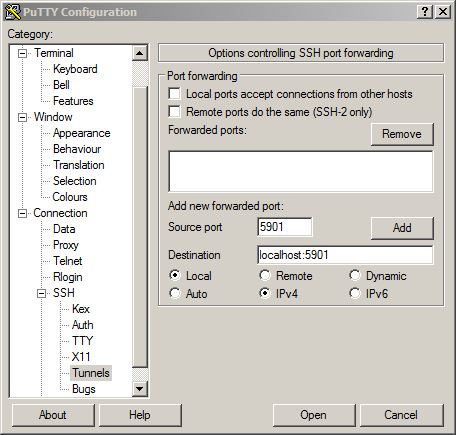
After clicking the "Add"-Button the putty window changes to:
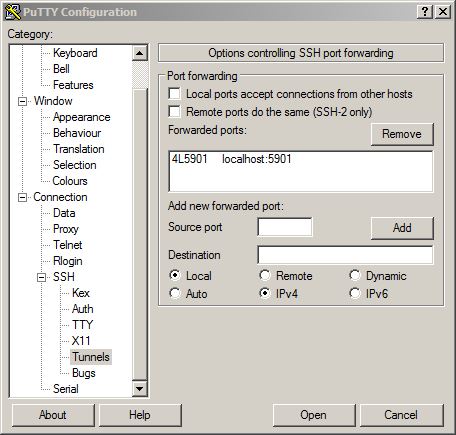
Don't forget to save the session if you want this tunnel to be permanently configured in this session.
Now you can connect your vnc viewer programm to the configured listening port of the putty client on the client machine: